Black pepper
Black pepper is produced from the still-green, unripe drupe of the pepper plant. The drupes are cooked briefly in hot water, both to clean them and to prepare them for drying. The heat ruptures cell walls in the pepper, speeding the work of browning enzymes during drying. The drupes dry in the sun or by machine for several days, during which the pepper skin around the seed shrinks and darkens into a thin, wrinkled black layer. Once dry, the spice is called black peppercorn. On some estates, the berries are separated from the stem by hand and then sun-dried without boiling. After the peppercorns are dried, pepper spirit and oil can be extracted from the berries by crushing them.
Science-Backed Health Benefits of Black Pepper
Black pepper contains antioxidants and may support your overall health. Benefits can include reducing inflammation and supporting blood sugar control and brain health, among others.
Black pepper is one of the most commonly used spices worldwide. It’s made by grinding peppercorns, which are dried berries from the vine Piper nigrum. It has a sharp and mildly spicy flavor that goes well with many dishes.
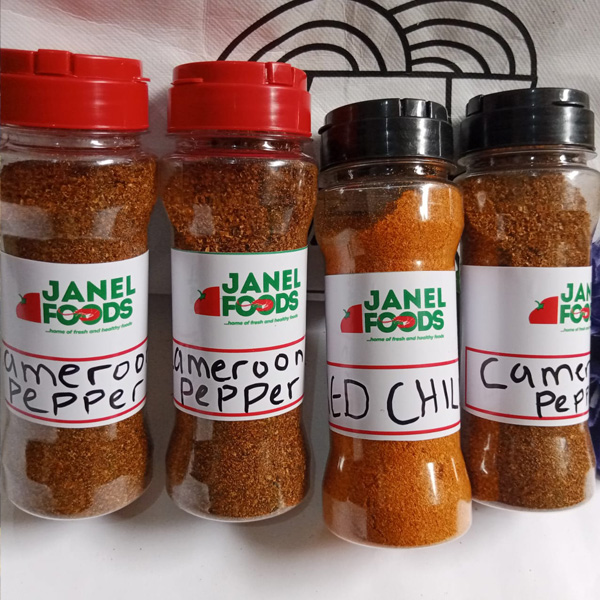
Cameroun Pepper
This is highly aromatic and hot pepper. Cameroon pepper adds distinct taste and a pungent spice of extra flavor to your meal, stews, sauces, soup, and traditional dishes.
The pepper has an active ingredient called piperine that is responsible for its distinct taste. A little addition of it give your meal the needed aroma and taste.
Red Chili Pepper
Maintains Blood Pressure – High content of potassium in red chili powder soothes blood vessels and regulates blood pressure. Rich Source Of Vitamin C – Vitamin C essentially supports the immune system and helps the body combat chronic diseases.
Food composition
Starch (33%), fats (7%), essential oil (1 – 2%), nitrogen compounds (12%) Piperine – an alkaloid, usually below 9%, responsible for the spiciness of pepper. It is contained both in the seed and in the pulp, especially in black pepper.
Healing effects
Pepper has digestive, anti-inflammatory and diuretic properties. It is used in case of anemia, diabetes and respiratory problems. The skins of pepper stimulates the absorption of fat by providing more energy to the body. Pepper can also have an external use on sebaceous glands. It is also used for relaxing and for rubbing muscles.
Culinary use
Pepper, depending on the type (white, black, green and red pepper) has a more or less pungent taste and aromatic smell.
It is used either in whole grains, or crushed and ground into fine powder to flavor a wide variety of dishes: soups, sauces, meat, fish, stews, salads, sausages and so on.
White pepper is used more traditionally in Western cuisine, while black pepper is the basic ingredient for a great variety of Eastern dishes. Typical recipes with green pepper, the delicate fillet. It is often mixed with other spices to flavor mixtures suitable for various types of meat and fish.
Since ancient times, pepper has been very useful for food preservation, especially for meat.
Preservation
Pepper grains keep their organoleptic properties longer than the ground or crushed pepper. Storage area must be cool, ventilated, poorly lit and dry.























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.